This database is described in
Please cite this publication when referencing this material, and also include the standard citation for PhysioNet:
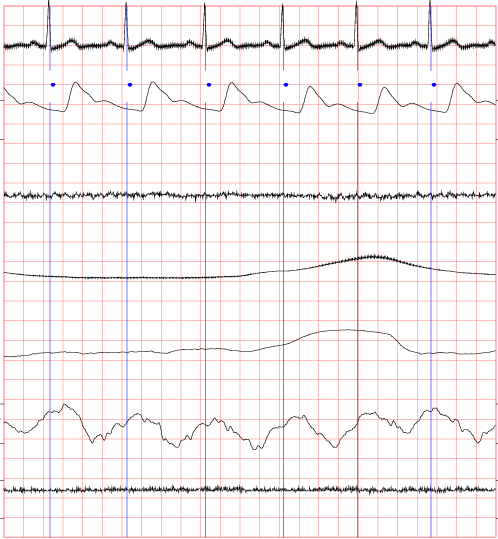
The MIT-BIH Polysomnographic Database is a collection of recordings of multiple physiologic signals during sleep. Subjects were monitored in Boston's Beth Israel Hospital Sleep Laboratory for evaluation of chronic obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, and to test the effects of constant positive airway pressure (CPAP), a standard therapeutic intervention that usually prevents or substantially reduces airway obstruction in these subjects. The database contains over 80 hours' worth of four-, six-, and seven-channel polysomnographic recordings, each with an ECG signal annotated beat-by-beat, and EEG and respiration signals annotated with respect to sleep stages and apnea. For further information, see Signals and Annotations.
The database consists of 18 records, each of which includes 4 files:
Andrew Walsh observed that the calibration originally provided for the BP signal of record slp37 is incorrect (since it yielded negative BPs). slp37.hea now contains an estimated BP calibration that yields more plausible BPs; these should not be regarded as accurate, however, since there is no independent calibration standard available for this recording.
|
If you would like help understanding, using, or downloading content, please see our Frequently Asked Questions. If you have any comments, feedback, or particular questions regarding this page, please send them to the webmaster. Comments and issues can also be raised on PhysioNet's GitHub page. Updated Tuesday, 4 October 2016 at 15:25 EDT |
PhysioNet is supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) and the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) under NIH grant number 2R01GM104987-09.
|